The best alternative to Clari
When it comes to driving your company's revenue strategy, the choice between Kluster and Clari matters. Forward-thinking companies choose Kluster.
| 4.5 200+ Reviews |
Get more bang for your buck
Our plans are simple. All our pricing includes customizing our platform for your unique business requirements, integrations, comprehensive onboarding, and ongoing dedicated support.No overages, just transparent, value-driven pricing.
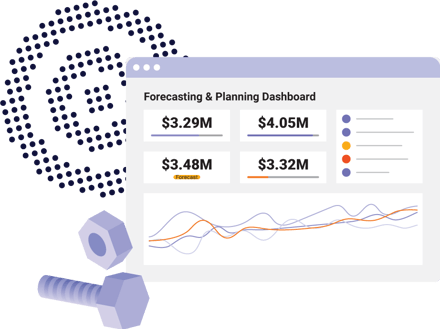
The flexibility you deserve
We understandsthat one size does not fit all. Unlike Ebsta's technical rigidity, Kluster's platform adapts to your unique requirements. Whether it's viewing annual forecasts or dissecting forecast splits, Kluster's flexibility ensures that your forecasting adapts to your business, not the other way around.
Reliability in Complexity
For an enterprise of Kpler's caliber, 'standard' solutions don't cut it. Kluster thrives where others falter, handling complex and custom datasets with ease. Trust in a forecasting solution built to handle the intricacies of your business landscape.
The Ultimate Executive Guide to Sales KPIs: Key Metrics for Strategic Decision-Making
Empower your board and leadership team with comprehensive insights, best practices, and critical sales metrics
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Introduction
Key Sales KPIs Covered in This Guide
-
Number of Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days
-
Number of Opportunities Created
-
% of Sales Bookings in Months 1, 2, 3 of the Quarter
-
AACV of Customer Base
-
AACV of Pipeline Created
-
Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR)
-
Best Case Revenue Forecast This Quarter
-
Biggest New Business Deal Per Quarter
-
Contracted Annual Recurring Revenue (CARR)
-
Commit Revenue Forecast This Quarter
-
Contribution Forecast Future Quarters
-
Contraction In-Quarter
-
Create and Close Metrics
-
Demand Generation Forecast
-
Difference Between Pipeline AACV and Customer AACV
-
Expected Forecast Future Quarters
-
Expansion In-Quarter
-
Fastest Deal Per Quarter
-
Forecast AACV of Customers
-
Future Quarters Pipeline Coverage Requirements
-
Gross Revenue Retention (GRR)
-
GRR Waterfall / Bridge with Explanation
-
Median New Business Deal Per Quarter
-
Median Sales Cycle Per Quarter
-
Meetings / Demos Booked
-
Meetings / Demos Held
-
Net Revenue Retention (NRR)
-
NRR Waterfall / Bridge with Explanation
-
Pipeline Created
-
Pipeline Open Per Stage Forecast for Day 1 of Next Quarter, Closing in Next Quarter
-
Pipeline Open Per Stage on Day 1 of Quarter, Closing in Quarter
-
Pipeline Open Per Stage Today, Closing in Quarter
-
Pipeline Win Rate (#/$)
-
Renewal Forecast Future Quarters (#/$)
-
Renewal Forecast In-Quarter (#/$)
-
Revenue Added Next Quarter
-
Revenue Added This Quarter
-
Revenue Forecast Accuracy Over Time
-
REVENUE FORECAST FUTURE QUARTERS (4 INDEPENDENT WAYS, MINIMUM)
-
Revenue Forecast This Quarter (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
-
Sales and Revenue Forecasts Versus Plan, Full Historic Audit Tracking
-
Sales Bookings "Best Case" Forecast This Quarter
-
Sales Bookings "Commit" Forecast This Quarter
-
Sales Bookings Forecast Future Quarters (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
-
Sales Bookings Forecast This Quarter (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
-
Sales Bookings Forecast Using Demand Generation Forecast as Base
-
Sales Bookings to Date
-
Sales Cycle
-
Sales Forecast Accuracy Over Time [0.5 to 5 Sales Cycles Out]
-
Sales Velocity
-
Sales-to-Revenue Recognition Walkthrough [Waterfall, Bridge or Similar with Explanation of Each Step]
-
Slipped Pipeline from Last Quarter to This Quarter
-
Slipped Pipeline from This Quarter to Next Quarter
-
Slowest Deal Per Quarter
-
Smallest New Business Deal Per Quarter
-
Stage Weighted Pipeline
-
Stage Win Rates (#/$)
-
Weighted Pipeline
-
Win Rate (#/$)
Introduction
In the competitive world of sales, understanding and effectively managing key performance indicators (KPIs) is essential for strategic decision-making. KPIs are measurable values that indicate how well a company is achieving its business objectives. For sales teams, these metrics provide critical insights into performance, efficiency, and growth potential.
This comprehensive guide is designed specifically for executives and board members who need to understand, track, and leverage sales KPIs. Whether you're a CEO looking to drive revenue growth, a CFO managing financial health, or a board member overseeing company performance, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need.
How to Use This Guide
Each KPI in this guide includes a detailed definition, its importance, how to use it, linked metrics, and best practices for implementation. This structure ensures you not only grasp what each KPI represents but also understand how they interrelate and contribute to overall business success.
- Definitions: Clear explanations of what each KPI measures.
- Importance: Insights into why each KPI is crucial for your business.
- Usage: Guidelines on how often to track and review each KPI.
- Linked Metrics: Connections to other relevant KPIs to provide a holistic view.
- Best Practices: Practical tips to maximize the effectiveness of each KPI.
75%
of respondents say staff fabricates data to tell the story they want decision makers to hear.
Definition: Deals expected to close within the next 90 days.
Importance: Indicates short-term revenue potential, helping to forecast immediate cash flow.
Use: Track daily. Should be increasing to show a healthy pipeline.
Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Win Rate: To understand the likelihood of closing these opportunities.
- Commit Revenue Forecast: To gauge how these opportunities contribute to committed revenue.
Best Practices:
- Regular Updates: Update and review with the sales team regularly.
- Focus on Progress: Ensure that these opportunities are moving through the sales stages promptly.
- Remove Stagnant Deals: Regularly clean up the pipeline by removing stagnant deals.
Number of Opportunities Created
Definition: Number of new sales opportunities generated.
Importance: Measures lead generation effectiveness and market demand.
Use: Track weekly and monthly to monitor trends and adjust strategies.
Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Created: Indicates how many of these opportunities enter the sales pipeline.
- Demand Generation Forecast: Aligns with the effectiveness of lead generation campaigns.
Best Practices:
- Diversify Sources: Ensure a steady flow through diverse channels like inbound marketing, outbound sales, and referrals.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on the quality of opportunities to increase conversion rates.
- Consistent Tracking: Regularly review the sources and types of opportunities created to refine lead generation strategies.
% of Sales Bookings in Months 1, 2, 3 of the Quarter
Definition: Percentage of total sales bookings achieved each month in the quarter.
Importance: Shows sales distribution over the quarter, helping to identify sales cycle patterns.
Use: Track monthly to balance effort and resources.
Linked Metrics:
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Tracks the actual revenue realized from these bookings.
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand how the sales cycle impacts monthly bookings.
Best Practices:
- Balanced Effort: Aim for balanced distribution to avoid end-of-quarter rush.
- Identify Patterns: Analyze patterns to understand when customers are most likely to purchase.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources effectively based on the booking trends.
AACV of Customer Base
Definition: Average Annual Contract Value of your current customers.
Importance: Indicates customer value and revenue stability over time.
Use: Review quarterly to track customer growth and retention.
Linked Metrics:
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): Measures how well you retain and grow existing customers.
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Indicates retention without upsells or cross-sells.
Best Practices:
- Increase Value: Focus on increasing AACV through upselling and cross-selling.
- Customer Segmentation: Segment customers by value to tailor retention and growth strategies.
- Monitor Churn: Keep an eye on customer churn rates and address issues promptly.
AACV of Pipeline Created
Definition: Average Annual Contract Value of new opportunities in the pipeline.
Importance: Predicts future revenue potential based on new leads.
Use: Track monthly to gauge the quality of the pipeline.
Linked Metrics:
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Helps predict near-term revenue potential.
- Revenue Forecast Future Quarters: Indicates potential future revenue from the pipeline.
Best Practices:
- High-Value Focus: Focus on high-value opportunities to maximize revenue.
- Pipeline Health: Ensure the pipeline is filled with opportunities that have a high probability of closing.
- Regular Analysis: Analyze the pipeline regularly to identify and remove low-value or low-probability opportunities.
ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue)
Definition: Revenue from subscription-based services, annualized.
Importance: Key metric for subscription businesses, indicating long-term financial health.
Use: Review monthly to track growth and retention.
Linked Metrics:
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): To measure the overall growth of recurring revenue.
- CARR (Contracted Annual Recurring Revenue): To understand the total value of contracted recurring revenue.
Best Practices:
- Consistent Growth: Aim for consistent ARR growth through renewals and new subscriptions.
- Customer Retention: Implement strong retention strategies to minimize churn.
- Upsell Opportunities: Identify and capitalize on upsell opportunities within the existing customer base.
Best Case Revenue Forecast This Quarter
Definition: Optimistic revenue projection for the current quarter.
Importance: Helps set upper expectations and identifies potential maximum revenue.
Use: Update bi-weekly to adjust for market and sales changes.
Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a conservative baseline to compare against the best case.
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Tracks the actual revenue realized against the forecast.
Best Practices:
- Realistic Assumptions: Use realistic assumptions to avoid overestimation.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for different scenarios to manage expectations and plan accordingly.
- Regular Updates: Keep the forecast updated with the latest sales data and market trends.
Biggest New Business Deal Per Quarter
Definition: The largest new deal closed in the quarter.
Importance: Highlights major wins and sales efforts.
Use: Track quarterly to showcase success and set benchmarks.
Linked Metrics:
- Median New Business Deal Per Quarter: Provides context on the range and typical size of deals.
- Sales Bookings Forecast: Helps in understanding the contribution of large deals to overall sales.
Best Practices:
- Celebrate Wins: Celebrate and analyze to replicate success.
- Analyze Factors: Understand the factors that contributed to closing the deal.
- Leverage Learnings: Use learnings to improve overall sales strategies.
CARR (Contracted Annual Recurring Revenue)
Definition: Total contracted revenue annualized.
Importance: Measures future revenue stability from long-term contracts.
Use: Review quarterly to ensure ongoing revenue stability.
Linked Metrics:
- ARR (Annual Recurring Revenue): Provides insight into the growth of recurring revenue.
- Customer Retention Rates: Helps understand the stability and potential growth of CARR.
Best Practices:
- Long-Term Contracts: Increase CARR through long-term contracts.
- Customer Loyalty: Focus on building long-term customer relationships.
- Monitor Renewals: Regularly monitor contract renewals to maintain CARR.
Commit Revenue Forecast This Quarter
Definition: Revenue forecast based on committed deals.
Importance: Sets minimum expected revenue, providing a conservative baseline.
Use: Update weekly to ensure accuracy.
Linked Metrics:
- Best Case Revenue Forecast: Compare to understand the range of revenue expectations.
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Tracks the actual revenue realized against the forecast.
Best Practices:
- Conservative Estimates: Use conservative estimates to set a reliable baseline.
- Regular Updates: Update the forecast with new data and changes in the pipeline.
- Close Monitoring: Closely monitor committed deals to ensure they progress towards closure.
Contribution Forecast Future Quarters (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Expected number and value of deals contributing to future quarters.
Importance: Helps in long-term planning and resource allocation.
Use: Update monthly to ensure accurate forecasting.
Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Created: Indicates how new opportunities will affect future contributions.
- Revenue Forecast Future Quarters: Ensures alignment with overall revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts current with the latest data.
- Trend Analysis: Analyze trends to improve future predictions.
- Adjust Strategies: Use insights to adjust sales and marketing strategies as needed.
Contribution Forecast In-Quarter (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Projected number and value of deals contributing within the current quarter.
Importance: Provides a near-term view of expected revenue.
Use: Track weekly to monitor progress.
Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Compare to ensure alignment with committed deals.
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Helps gauge immediate revenue potential.
Best Practices:
- Close Monitoring: Keep a close watch on deal progression.
- Adjust Tactics: Adjust sales tactics based on forecast performance.
- Communicate Progress: Regularly communicate progress to relevant stakeholders.
Contraction In-Quarter (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Number and value of contracts that are expected to shrink within the current quarter.
Importance: Identifies potential revenue losses and areas needing attention.
Use: Track quarterly to address issues promptly.
Linked Metrics:
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Provides insight into overall revenue retention.
- Customer Churn Rate: Helps understand the factors driving contractions.
Best Practices:
- Identify Causes: Quickly identify and address the causes of contraction.
- Retention Strategies: Implement strategies to retain at-risk customers.
- Customer Feedback: Gather and act on customer feedback to prevent future contractions.
Create and Close: Ability to Calculate Daily
Definition: Ability to create and close deals within the same period.
Importance: Shows efficiency and effectiveness of the sales process.
Use: Track daily for real-time insights.
Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Helps measure and improve the speed of the sales process.
- Sales Velocity: Indicates how quickly revenue is generated.
Best Practices:
- Process Optimization: Continuously optimize the sales process for faster closes.
- Quick Wins: Focus on quick wins to maintain momentum.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor sales performance daily to identify bottlenecks.
Demand Generation Forecast (Future 4 Quarters)
Definition: Expected leads, meetings, and demos over the next four quarters.
Importance: Indicates future sales potential and helps in planning.
Use: Review quarterly to adjust strategies.
Linked Metrics:
- Opportunities Created: Directly impacts the number of new opportunities.
- Pipeline Created: Reflects how demand generation efforts fill the pipeline.
Best Practices:
- Integrated Strategies: Align marketing and sales strategies for consistent demand generation.
- Regular Review: Regularly review and adjust forecasts based on performance.
- Focus on Quality: Ensure the quality of leads to improve conversion rates.
Difference Pipeline AACV and Customer AACV
Definition: Difference between AACV of pipeline and current customers. Importance: Shows growth potential and pipeline quality.
Use: Track monthly to monitor trends. Linked Metrics:
- AACV of Customer Base: Provides context on the value of existing customers.
- AACV of Pipeline Created: Indicates the potential value of new opportunities.
Best Practices:
- Gap Analysis: Perform regular gap analysis to identify growth opportunities.
- Optimize Pipeline: Focus on high-value opportunities to increase AACV.
- Customer Segmentation: Segment customers and opportunities to tailor strategies.
Expected Forecast Future Quarters (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Projected number and value of deals for future quarters. Importance: Predicts future performance and guides resource allocation. Use: Review quarterly to adjust long-term plans. Linked Metrics:
- Contribution Forecast Future Quarters: Ensures alignment with expected contributions.
- Pipeline Created: Provides insight into the source of future deals.
Best Practices:
- Accurate Data: Ensure data accuracy for reliable forecasts.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for different scenarios to manage risks.
- Strategic Adjustments: Use insights to make strategic adjustments as needed.
Expected Forecast In-Quarter (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Projected number and value of deals for the current quarter. Importance: Provides a short-term view of expected revenue. Use: Track weekly to monitor performance. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Compare to committed deals for alignment.
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Helps predict immediate revenue.
Best Practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts current with the latest data.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor performance closely to address issues promptly.
- Adjust Tactics: Adjust sales tactics based on forecast performance.
Expansion In-Quarter (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Number and value of expansions within the current quarter. Importance: Indicates upsell and cross-sell success. Use: Track quarterly to identify growth opportunities. Linked Metrics:
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): Reflects the impact of expansions on overall revenue.
- Customer Segmentation: Helps identify which customer segments are expanding.
Best Practices:
- Identify Opportunities: Proactively identify upsell and cross-sell opportunities.
- Customer Engagement: Engage with customers to understand their needs and offer relevant solutions.
- Track Success: Monitor the success of expansion efforts and adjust strategies accordingly.
Fastest Deal Per Quarter
Definition: Quickest deal from creation to close in the quarter. Importance: Shows sales efficiency and potential best practices. Use: Track quarterly to identify effective sales strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the factors contributing to quick closes.
- Sales Velocity: Indicates overall speed of revenue generation.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Success: Analyze the factors that contributed to fast closes.
- Replicate Best Practices: Replicate successful strategies across the sales team.
- Continuous Improvement: Continuously improve processes to reduce the sales cycle.
Forecast AACV of Customers
Definition: Projected AACV of current customers. Importance: Indicates future revenue from existing customers. Use: Review quarterly to adjust retention and growth strategies. Linked Metrics:
- AACV of Customer Base: Provides a baseline for future projections.
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): Reflects the impact of customer growth on revenue.
Best Practices:
- Retention Focus: Focus on customer retention to maintain and grow AACV.
- Growth Strategies: Implement strategies to grow AACV through upselling and cross-selling.
- Monitor Trends: Regularly monitor trends to adjust forecasts and strategies.
Future Quarters Pipeline Coverage Requirements
Definition: Needed pipeline to meet future revenue targets. Importance: Ensures future revenue targets are met and guides resource allocation. Use: Update weekly to adjust plans. Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Created: Provides insight into the source of future opportunities.
- Expected Forecast Future Quarters: Ensures alignment with future revenue projections.
Best Practices:
- Regular Updates: Keep pipeline coverage requirements current with the latest data.
- Resource Allocation: Allocate resources effectively based on coverage requirements.
- Performance Monitoring: Monitor performance to ensure targets are met.
GRR (Gross Revenue Retention)
Definition: Revenue retained from existing customers, excluding upsells. Importance: Measures customer loyalty and retention. Use: Track monthly to monitor retention performance. Linked Metrics:
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): Provides a complete picture of revenue retention, including upsells.
- Customer Churn Rate: Helps understand the factors driving retention.
Best Practices:
- Retention Strategies: Implement strong retention strategies to minimize churn.
- Customer Engagement: Engage with customers to ensure satisfaction and loyalty.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor retention performance to address issues promptly.
GRR Waterfall / Bridge with Explanation
Definition: Breakdown of changes in GRR over time. Importance: Understands retention dynamics and identifies areas for improvement. Use: Review quarterly to analyze trends. Linked Metrics:
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Provides the overall retention rate.
- Customer Feedback: Helps identify the reasons behind retention changes.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Trends: Regularly analyze trends to identify areas for improvement.
- Implement Changes: Implement changes based on insights from the analysis.
- Customer Feedback: Gather and act on customer feedback to improve retention.
Median New Business Deal Per Quarter
Definition: Middle value of new deals closed each quarter. Importance: Indicates typical deal size and helps in setting expectations. Use: Track quarterly to monitor deal size trends. Linked Metrics:
- Biggest New Business Deal Per Quarter: Provides context on the range of deal sizes.
- Sales Bookings Forecast: Helps in understanding the contribution of typical deals to overall sales.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Trends: Regularly analyze trends to understand changes in deal sizes.
- Set Expectations: Use median deal size to set realistic sales expectations.
- Focus on Growth: Implement strategies to increase the median deal size.
Median Sales Cycle Per Quarter
Definition: Typical time taken to close a deal. Importance: Measures sales process efficiency and helps identify bottlenecks. Use: Track quarterly to monitor changes in the sales cycle. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Provides a detailed view of the time taken to close deals.
- Sales Velocity: Indicates overall speed of revenue generation.
Best Practices:
- Process Optimization: Continuously optimize the sales process to reduce the cycle time.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Identify and address bottlenecks in the sales process.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
Meetings / Demos Booked
Definition: Number of meetings and demos scheduled. Importance: Indicates engagement and interest from prospects. Use: Track weekly to monitor lead engagement. Linked Metrics:
- Opportunities Created: Reflects the effectiveness of meetings and demos in generating opportunities.
- Demand Generation Forecast: Aligns with the efforts to generate interest and leads.
Best Practices:
- High Engagement: Aim for high engagement by scheduling frequent meetings and demos.
- Follow-Up: Ensure effective follow-up to convert meetings and demos into opportunities.
- Track Success: Monitor the success rate of meetings and demos in generating leads.
Meetings / Demos Held
Definition: Number of meetings and demos completed. Importance: Measures actual engagement and effectiveness. Use: Track weekly to monitor lead engagement. Linked Metrics:
- Opportunities Created: Reflects the effectiveness of meetings and demos in generating opportunities.
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the impact of meetings and demos on the sales cycle.
Best Practices:
- High Completion Rate: Aim for a high completion rate of scheduled meetings and demos.
- Effective Presentations: Ensure that meetings and demos are effective in engaging prospects.
- Monitor Results: Monitor the results of meetings and demos to improve future efforts.
NRR (Net Revenue Retention)
Definition: Revenue retained, including upsells and cross-sells. Importance: Measures overall growth and customer loyalty. Use: Track monthly to monitor revenue retention. Linked Metrics:
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Provides insight into revenue retention excluding upsells.
- Expansion In-Quarter: Reflects the impact of upsells and cross-sells on NRR.
Best Practices:
- Retention Focus: Focus on retaining and growing existing customers.
- Upsell Strategies: Implement effective upsell and cross-sell strategies.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to address issues promptly.
NRR Waterfall / Bridge with Explanation
Definition: Breakdown of changes in NRR over time. Importance: Understands growth dynamics and identifies areas for improvement. Use: Review quarterly to analyze trends. Linked Metrics:
- NRR (Net Revenue Retention): Provides the overall retention rate.
- Customer Feedback: Helps identify the reasons behind retention changes.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Trends: Regularly analyze trends to identify areas for improvement.
- Implement Changes: Implement changes based on insights from the analysis.
- Customer Feedback: Gather and act on customer feedback to improve retention.
Pipeline Created
Definition: New opportunities added to the pipeline. Importance: Measures lead generation success and future sales potential. Use: Track monthly to monitor trends and adjust strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Opportunities Created: Indicates the effectiveness of lead generation efforts.
- Demand Generation Forecast: Aligns with the efforts to generate interest and leads.
Best Practices:
- Steady Flow: Ensure a steady flow of new opportunities into the pipeline.
- Quality Leads: Focus on generating high-quality leads to improve conversion rates.
- Track Success: Monitor the success of pipeline creation efforts to adjust strategies.
Pipeline Open Per Stage Forecast for Day 1 of Next Quarter, Closing in Next Quarter
Definition: Opportunities in each stage of the pipeline expected to close in the next quarter. Importance: Helps forecast near-term revenue and manage sales efforts. Use: Track quarterly to adjust strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Provides insight into near-term revenue potential.
- Pipeline Win Rate: Helps predict the likelihood of closing these opportunities.
Best Practices:
- Balanced Pipeline: Ensure a balanced pipeline across stages for smooth progression.
- Focus on Progress: Focus on progressing opportunities through the stages promptly.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update forecasts to ensure accuracy.
Pipeline Open Per Stage Today, Closing in Quarter
Definition: Opportunities in each stage of the pipeline expected to close in the current quarter. Importance: Helps manage sales efforts and forecast near-term revenue. Use: Track daily to adjust strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Provides insight into near-term revenue potential.
- Pipeline Win Rate: Helps predict the likelihood of closing these opportunities.
Best Practices:
- Balanced Pipeline: Ensure a balanced pipeline across stages for smooth progression.
- Focus on Progress: Focus on progressing opportunities through the stages promptly.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update forecasts to ensure accuracy.
Pipeline Win Rate (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Percentage of opportunities won, by count and value. Importance: Measures sales effectiveness and forecast accuracy. Use: Track monthly to monitor performance. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the impact of win rates on the sales cycle.
- Revenue Forecast Accuracy: Indicates the reliability of revenue forecasts.
Best Practices:
- Improve Techniques: Implement techniques to improve win rates.
- Analyze Losses: Analyze lost opportunities to identify and address issues.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
Renewal Forecast Future Quarters (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Projected renewals, by count and value, for future quarters. Importance: Indicates future revenue stability and customer retention. Use: Track quarterly to adjust retention strategies. Linked Metrics:
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Provides insight into overall revenue retention.
- Customer Retention Rates: Helps understand the factors driving renewals.
Best Practices:
- Retention Focus: Focus on retaining existing customers to ensure renewals.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to address issues promptly.
- Engage Customers: Engage with customers to ensure satisfaction and loyalty.
Renewal Forecast In-Quarter (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Projected renewals, by count and value, for the current quarter. Importance: Indicates near-term revenue stability and customer retention. Use: Track quarterly to adjust retention strategies. Linked Metrics:
- GRR (Gross Revenue Retention): Provides insight into overall revenue retention.
- Customer Retention Rates: Helps understand the factors driving renewals.
Best Practices:
- Retention Focus: Focus on retaining existing customers to ensure renewals.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to address issues promptly.
- Engage Customers: Engage with customers to ensure satisfaction and loyalty.
Revenue Added Next Quarter
Definition: New revenue expected to be generated in the next quarter. Importance: Shows future growth potential and guides resource allocation. Use: Track quarterly to adjust strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Created: Provides insight into the source of new revenue.
- Expected Forecast Future Quarters: Ensures alignment with future revenue projections.
Best Practices:
- Focus on Growth: Implement strategies to maximize revenue growth.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to address issues promptly.
- Adjust Strategies: Adjust strategies based on performance and market conditions.
Revenue Added This Quarter
Definition: New revenue generated in the current quarter. Importance: Shows immediate growth and performance. Use: Track quarterly to adjust strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for expected revenue.
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Helps predict near-term revenue.
Best Practices:
- Focus on Growth: Implement strategies to maximize revenue growth.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to address issues promptly.
- Adjust Strategies: Adjust strategies based on performance and market conditions.
Revenue Forecast Accuracy Over Time
Definition: Precision of revenue forecasts over time. Importance: Indicates forecasting reliability and helps improve future predictions. Use: Track quarterly to monitor accuracy. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for comparison.
- Best Case Revenue Forecast: Helps understand the range of revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Accuracy: Regularly analyze forecast accuracy to identify areas for improvement.
- Refine Methods: Refine forecasting methods based on analysis.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Revenue Forecast Future Quarters (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
Definition: Revenue forecasts for future quarters using at least four different methods. Importance: Ensures comprehensive and accurate forecasting. Use: Review quarterly to adjust long-term plans. Linked Metrics:
- Expected Forecast Future Quarters: Ensures alignment with overall revenue projections.
- Pipeline Created: Provides insight into the source of future revenue.
Best Practices:
- Use Multiple Methods: Use diverse methods for more accurate forecasts.
- Compare Results: Compare results from different methods to identify trends.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Revenue Forecast This Quarter (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
Definition: Revenue forecasts for the current quarter using at least four different methods. Importance: Ensures comprehensive and accurate forecasting. Use: Review quarterly to adjust short-term plans. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for comparison.
- Best Case Revenue Forecast: Helps understand the range of revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Use Multiple Methods: Use diverse methods for more accurate forecasts.
- Compare Results: Compare results from different methods to identify trends.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Sales and Revenue Forecasts Versus Plan, Full Historic Audit Tracking
Definition: Comparison of sales and revenue forecasts against the plan with historic tracking. Importance: Provides insights into forecast accuracy and helps identify areas for improvement. Use: Track quarterly to monitor performance. Linked Metrics:
- Revenue Forecast Accuracy Over Time: Indicates the reliability of revenue forecasts.
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for comparison.
Best Practices:
- Historical Analysis: Perform regular historical analysis to identify trends.
- Improve Accuracy: Implement changes to improve forecasting accuracy.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Sales Bookings "Best Case" Forecast This Quarter
Definition: Optimistic revenue projection for sales bookings in the current quarter. Importance: Helps set upper expectations and identifies potential maximum revenue. Use: Update bi-weekly to adjust for market and sales changes. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a conservative baseline to compare against the best case.
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Tracks the actual revenue realized against the forecast.
Best Practices:
- Realistic Assumptions: Use realistic assumptions to avoid overestimation.
- Scenario Planning: Prepare for different scenarios to manage expectations and plan accordingly.
- Regular Updates: Keep the forecast updated with the latest sales data and market trends.
Sales Bookings "Commit" Forecast This Quarter
Definition: Revenue forecast based on committed deals. Importance: Sets minimum expected revenue, providing a conservative baseline. Use: Update weekly to ensure accuracy. Linked Metrics:
- Best Case Revenue Forecast: Compare to understand the range of revenue expectations.
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Tracks the actual revenue realized against the forecast.
Best Practices:
- Conservative Estimates: Use conservative estimates to set a reliable baseline.
- Regular Updates: Update the forecast with new data and changes in the pipeline.
- Close Monitoring: Closely monitor committed deals to ensure they progress towards closure.
Sales Bookings Forecast Future Quarters (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
Definition: Revenue forecasts for future quarters using at least four different methods. Importance: Ensures comprehensive and accurate forecasting. Use: Review quarterly to adjust long-term plans. Linked Metrics:
- Expected Forecast Future Quarters: Ensures alignment with overall revenue projections.
- Pipeline Created: Provides insight into the source of future revenue.
Best Practices:
- Use Multiple Methods: Use diverse methods for more accurate forecasts.
- Compare Results: Compare results from different methods to identify trends.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Sales Bookings Forecast This Quarter (4 Independent Ways, Minimum)
Definition: Revenue forecasts for the current quarter using at least four different methods. Importance: Ensures comprehensive and accurate forecasting. Use: Review quarterly to adjust short-term plans. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for comparison.
- Best Case Revenue Forecast: Helps understand the range of revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Use Multiple Methods: Use diverse methods for more accurate forecasts.
- Compare Results: Compare results from different methods to identify trends.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Sales Bookings Forecast Using Demand Generation Forecast as Base
Definition: Revenue forecasts based on expected leads, meetings, and demos from demand generation efforts. Importance: Ensures that sales forecasts are grounded in demand generation activities. Use: Review quarterly to adjust strategies. Linked Metrics:
- Demand Generation Forecast: Provides the base data for sales bookings forecasts.
- Pipeline Created: Reflects the impact of demand generation efforts on the pipeline.
Best Practices:
- Align Strategies: Align marketing and sales strategies to ensure consistent demand generation.
- Monitor Conversion: Monitor conversion rates from leads to sales to improve accuracy.
- Adjust Forecasts: Adjust forecasts based on the performance of demand generation efforts.
Sales Bookings to Date
Definition: Total sales bookings achieved to date in the current period. Importance: Provides a real-time view of sales performance. Use: Track daily to monitor progress. Linked Metrics:
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Tracks the actual revenue realized from bookings.
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for expected revenue.
Best Practices:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Monitor sales bookings in real-time to address issues promptly.
- Adjust Strategies: Adjust sales strategies based on performance to date.
- Communicate Progress: Regularly communicate progress to relevant stakeholders.
Sales Cycle
Definition: Time taken from opportunity creation to close. Importance: Measures sales process efficiency and helps identify bottlenecks. Use: Track monthly to monitor changes in the sales cycle. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Velocity: Indicates overall speed of revenue generation.
- Median Sales Cycle: Provides a typical time frame for closing deals.
Best Practices:
- Process Optimization: Continuously optimize the sales process to reduce the cycle time.
- Identify Bottlenecks: Identify and address bottlenecks in the sales process.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
Sales Forecast Accuracy Over Time [0.5 to 5 Sales Cycles Out]
Definition: Precision of sales forecasts over different time frames. Importance: Indicates forecasting reliability and helps improve future predictions. Use: Track quarterly to monitor accuracy. Linked Metrics:
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for comparison.
- Best Case Revenue Forecast: Helps understand the range of revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Accuracy: Regularly analyze forecast accuracy to identify areas for improvement.
- Refine Methods: Refine forecasting methods based on analysis.
- Regular Updates: Keep forecasts updated with the latest data and trends.
Sales Velocity
Definition: Speed at which revenue is generated. Importance: Indicates overall sales efficiency and growth potential. Use: Track monthly to monitor performance. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the impact of sales velocity on the sales process.
- Revenue Added This Quarter: Reflects the speed of revenue generation.
Best Practices:
- Improve Techniques: Implement techniques to improve sales velocity.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
- Adjust Strategies: Adjust strategies based on performance and market conditions.
Sales-to-Revenue Recognition Walkthrough [Waterfall, Bridge or Similar with Explanation of Each Step]
Definition: Detailed process explaining how sales bookings translate into recognized revenue. Importance: Provides clarity on revenue recognition and helps manage expectations. Use: Review quarterly to ensure accuracy and compliance. Linked Metrics:
- Revenue Forecast Accuracy: Ensures alignment between sales bookings and revenue recognition.
- Commit Revenue Forecast: Provides a baseline for expected revenue.
Best Practices:
- Detailed Documentation: Maintain detailed documentation of the sales-to-revenue recognition process.
- Regular Review: Regularly review the process to ensure accuracy and compliance.
- Communicate Changes: Communicate any changes in the process to relevant stakeholders.
Slipped Pipeline from Last Quarter to This Quarter
Definition: Opportunities that were expected to close last quarter but slipped into the current quarter. Importance: Indicates potential issues in the sales process and helps adjust strategies. Use: Track quarterly to address issues promptly. Linked Metrics:
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Provides insight into near-term revenue potential.
- Pipeline Win Rate: Helps understand the likelihood of closing slipped opportunities.
Best Practices:
- Identify Causes: Quickly identify and address the causes of slipped opportunities.
- Adjust Tactics: Adjust sales tactics to improve close rates.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
Slipped Pipeline from This Quarter to Next Quarter
Definition: Opportunities that were expected to close this quarter but slipped into the next quarter. Importance: Indicates potential issues in the sales process and helps adjust strategies. Use: Track quarterly to address issues promptly. Linked Metrics:
- Open Opportunities Closing in 90 Days: Provides insight into near-term revenue potential.
- Pipeline Win Rate: Helps understand the likelihood of closing slipped opportunities.
Best Practices:
- Identify Causes: Quickly identify and address the causes of slipped opportunities.
- Adjust Tactics: Adjust sales tactics to improve close rates.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
Slowest Deal Per Quarter
Definition: Longest deal from creation to close in the quarter. Importance: Identifies bottlenecks and areas for process improvement. Use: Track quarterly to identify and address issues. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the factors contributing to long closes.
- Sales Velocity: Indicates overall speed of revenue generation.
Best Practices:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Identify the reasons for slow closes and address them.
- Process Improvement: Implement process improvements to speed up sales cycles.
- Monitor Progress: Regularly monitor progress to ensure continuous improvement.
Smallest New Business Deal Per Quarter
Definition: The smallest new deal closed in the quarter. Importance: Helps understand the range of deal sizes and potential for growth. Use: Track quarterly to monitor deal size trends. Linked Metrics:
- Median New Business Deal Per Quarter: Provides context on the range and typical size of deals.
- Sales Bookings Forecast: Helps in understanding the contribution of smaller deals to overall sales.
Best Practices:
- Analyze Trends: Regularly analyze trends to understand changes in deal sizes.
- Focus on Growth: Implement strategies to increase the size of new deals.
- Adjust Strategies: Adjust sales strategies based on deal size performance.
Stage Weighted Pipeline
Definition: Pipeline opportunities weighted by the probability of closing at each stage. Importance: Provides a realistic view of potential revenue. Use: Track monthly to monitor pipeline health. Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Win Rate: Helps understand the likelihood of closing opportunities at each stage.
- Revenue Forecast: Ensures alignment with overall revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Accurate Weighting: Ensure accurate weighting based on historical data and probabilities.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update the weighted pipeline to reflect the latest data.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of the weighted pipeline to identify areas for improvement.
Stage Win Rates (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Win rates by count and value for each stage of the pipeline. Importance: Measures sales effectiveness at different stages. Use: Track monthly to monitor performance. Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Win Rate: Provides a detailed view of win rates at each stage.
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the impact of stage win rates on the sales process.
Best Practices:
- Improve Techniques: Implement techniques to improve win rates at each stage.
- Analyze Losses: Analyze lost opportunities at each stage to identify and address issues.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.
Weighted Pipeline
Definition: Total pipeline opportunities weighted by the probability of closing. Importance: Provides a realistic view of potential revenue. Use: Track monthly to monitor pipeline health. Linked Metrics:
- Pipeline Win Rate: Helps understand the likelihood of closing opportunities.
- Revenue Forecast: Ensures alignment with overall revenue expectations.
Best Practices:
- Accurate Weighting: Ensure accurate weighting based on historical data and probabilities.
- Regular Updates: Regularly update the weighted pipeline to reflect the latest data.
- Monitor Performance: Monitor the performance of the weighted pipeline to identify areas for improvement.
Win Rate (Number and Dollar)
Definition: Percentage of opportunities won, by count and value. Importance: Measures sales effectiveness and forecast accuracy. Use: Track monthly to monitor performance. Linked Metrics:
- Sales Cycle: Helps understand the impact of win rates on the sales process.
- Revenue Forecast Accuracy: Indicates the reliability of revenue forecasts.
Best Practices:
- Improve Techniques: Implement techniques to improve win rates.
- Analyze Losses: Analyze lost opportunities to identify and address issues.
- Monitor Performance: Regularly monitor performance to ensure continuous improvement.